Maintaining a healthy gut is crucial for overall well-being. The gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome, which play a key role in digestion, immune function, mental health, and even disease prevention. A balanced and diverse gut microbiome is essential for optimal health, and what we eat has a direct impact on the composition and health of these gut bacteria. Incorporating specific foods into your diet can promote gut health, enhance digestion, and support a thriving microbiome.
In this article, we will explore the 15 best foods for gut health and microbiome support. These foods are rich in fiber, prebiotics, probiotics, and anti-inflammatory compounds that nourish your gut bacteria, improve digestion, and contribute to better overall health.
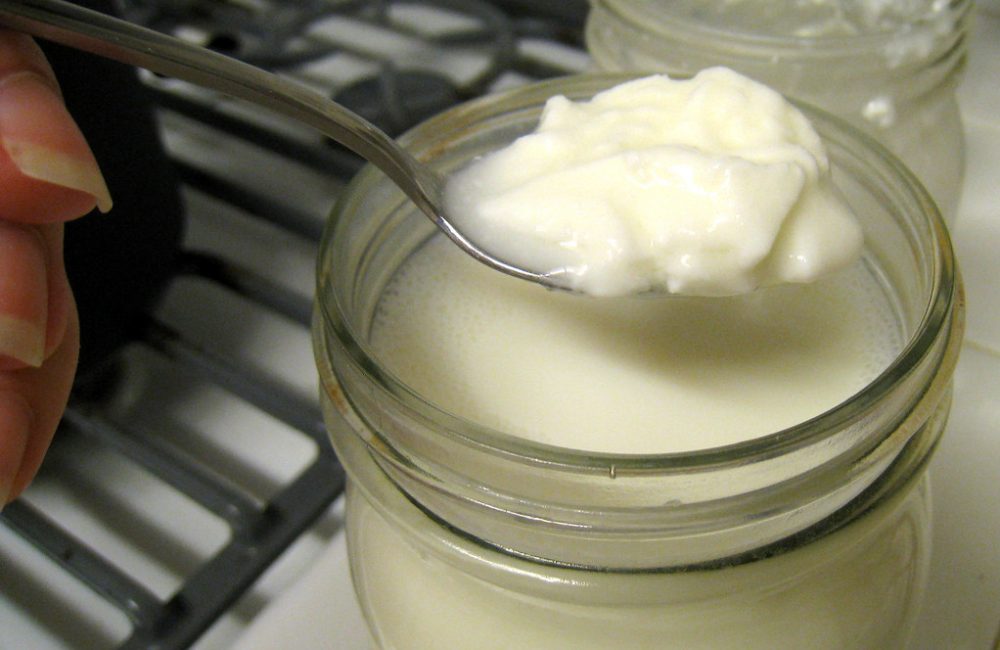
1. Yogurt
Yogurt is one of the most well-known foods for gut health, as it is a natural source of probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that help balance the gut microbiome. Probiotics in yogurt, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, help replenish good bacteria in the gut, promote healthy digestion, and reduce the symptoms of digestive issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
When choosing yogurt for gut health, it’s important to opt for plain, unsweetened varieties that contain live and active cultures. Flavored yogurts often contain added sugars, which can negatively affect gut health. Incorporating yogurt into your daily diet can provide a natural source of probiotics that support a healthy and balanced gut microbiome.
2. Kefir
Kefir is a fermented dairy product similar to yogurt, but it contains an even wider variety of probiotic bacteria and yeasts, making it an excellent choice for gut health. Kefir is known for its ability to support the diversity of the gut microbiome, which is essential for maintaining good digestion and preventing gut-related issues.
The probiotics in kefir help enhance digestion, reduce inflammation, and improve the body’s ability to absorb nutrients from food. Kefir is also rich in calcium, protein, and B vitamins, making it a nutritious addition to any gut-friendly diet. Drinking kefir regularly can help restore the balance of gut bacteria and promote a healthy digestive system.
3. Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut, which is fermented cabbage, is another powerful probiotic-rich food that can improve gut health. The fermentation process used to make sauerkraut produces beneficial bacteria that help populate the gut with healthy microbes. These probiotics aid in digestion, reduce gas and bloating, and support overall gut function.
In addition to probiotics, sauerkraut is rich in fiber, vitamin C, and antioxidants, which help reduce inflammation in the gut and promote a healthy digestive system. Including sauerkraut in your meals regularly can enhance the diversity of your gut microbiome and support healthy digestion.
4. Kimchi
Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, typically cabbage and radishes, and seasoned with spices. Like sauerkraut, kimchi is rich in probiotics, particularly Lactobacillus, which helps improve digestion and support gut health. The fermentation process also increases the nutritional value of kimchi, providing a good source of fiber, vitamin C, and antioxidants.
The probiotics in kimchi help balance the gut microbiome, reduce inflammation, and improve the body’s ability to break down food. Regular consumption of kimchi can support a healthy gut, improve digestion, and promote overall well-being.
5. Miso
Miso is a traditional Japanese fermented paste made from soybeans, salt, and koji (a type of fungus). It is often used to make miso soup and is a rich source of probiotics, particularly Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which support a healthy gut microbiome. Miso also contains enzymes that aid digestion and help break down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
The fermentation process that produces miso increases the levels of beneficial bacteria, which help maintain gut health by balancing the gut microbiome and promoting the growth of good bacteria. Adding miso to soups, sauces, or marinades can help support healthy digestion and improve gut function.
6. Tempeh
Tempeh is a fermented soybean product that is high in protein and rich in probiotics. The fermentation process used to make tempeh helps produce beneficial bacteria that promote gut health by improving digestion and supporting a balanced microbiome. Tempeh is also an excellent source of fiber, which helps feed the good bacteria in the gut.
In addition to its probiotic content, tempeh is rich in vitamins and minerals, including calcium, iron, and magnesium, all of which support overall health. Incorporating tempeh into your diet can help improve gut function, support digestion, and promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
7. Garlic
Garlic is a powerful prebiotic food, meaning it provides fuel for the beneficial bacteria in your gut, helping them thrive. Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed probiotics, making them essential for maintaining a healthy and diverse gut microbiome. Garlic contains compounds like inulin, a type of fiber that promotes the growth of good bacteria in the digestive tract.
In addition to its prebiotic benefits, garlic has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, which help reduce harmful bacteria in the gut and support overall gut health. Adding garlic to your meals regularly can enhance gut function and promote a healthy balance of bacteria.
8. Onions
Onions are another excellent source of prebiotics, particularly inulin and fructooligosaccharides (FOS), which help feed beneficial gut bacteria. These prebiotics promote the growth of healthy microbes in the gut and improve digestion by increasing the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are beneficial for gut health.
Onions also contain antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the gut. Including onions in your diet can help support a healthy microbiome and promote overall gut health.
9. Asparagus
Asparagus is rich in prebiotic fiber, particularly inulin, which supports the growth of good bacteria in the gut. This prebiotic fiber helps maintain a balanced gut microbiome, improves digestion, and supports healthy bowel movements. Asparagus is also high in antioxidants, which help protect the gut lining from oxidative damage and reduce inflammation.
In addition to supporting gut health, asparagus provides a good source of vitamins A, C, E, and K, as well as folate and iron, making it a nutrient-dense addition to your diet. Eating asparagus regularly can promote a healthy gut and improve overall digestive function.
10. Bananas
Bananas are a gut-friendly fruit that is rich in prebiotic fiber, particularly resistant starch, which feeds beneficial bacteria in the gut. This prebiotic fiber helps improve digestion, promote regular bowel movements, and support the growth of healthy gut bacteria. Bananas are also easy to digest, making them a great option for people with sensitive stomachs or digestive issues.
In addition to prebiotic fiber, bananas provide essential nutrients like potassium, which helps maintain healthy electrolyte balance and supports digestive health. Including bananas in your diet can promote gut health and improve overall digestion.
11. Apples
Apples are rich in pectin, a type of soluble fiber that acts as a prebiotic by feeding the good bacteria in your gut. Pectin helps promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, particularly Bifidobacteria, which are important for gut health and immune function. The fiber in apples also helps regulate digestion, improve bowel movements, and reduce inflammation in the gut.
In addition to their prebiotic benefits, apples contain antioxidants, including vitamin C and polyphenols, which help protect the gut from oxidative stress and inflammation. Eating apples regularly can help support a healthy gut microbiome and improve digestive health.
12. Oats
Oats are a rich source of beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that acts as a prebiotic and supports the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Beta-glucan helps improve digestion by promoting the production of short-chain fatty acids, which provide energy to the cells lining the gut and support overall gut health.
Oats also contain resistant starch, another type of prebiotic fiber that feeds good bacteria and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Including oats in your diet can promote a healthy microbiome, improve digestion, and support overall gut function.
13. Lentils
Lentils are high in fiber, particularly prebiotic fiber, which helps support the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. The fiber in lentils promotes regular bowel movements, improves digestion, and helps maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. Lentils are also rich in protein, iron, and folate, making them a nutritious addition to any gut-friendly diet.
In addition to their prebiotic benefits, lentils contain polyphenols, which have antioxidant properties that help reduce inflammation in the gut and support overall gut health. Eating lentils regularly can enhance digestion and promote a healthy gut microbiome.
14. Almonds
Almonds are a great source of prebiotic fiber, particularly oligosaccharides, which help feed the beneficial bacteria in the gut. The fiber in almonds supports healthy digestion, promotes regular bowel movements, and enhances the diversity of the gut microbiome. Almonds are also rich in healthy fats, vitamin E, and magnesium, which support overall health and reduce inflammation in the digestive tract.
In addition to their prebiotic benefits, almonds provide antioxidants that protect the gut lining from oxidative damage. Including almonds in your diet can help support a healthy gut and improve digestion.
15. Green Tea
Green tea contains polyphenols, particularly catechins, which have been shown to support gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing harmful bacteria. These polyphenols act as prebiotics, helping to feed the good bacteria in the gut and improve overall gut health.
In addition to its prebiotic effects, green tea has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help protect the gut from oxidative stress and inflammation. Drinking green tea regularly can support a healthy gut microbiome and promote better digestion.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall health, and incorporating gut-friendly foods into your diet can help support a balanced and diverse microbiome. The 15 best foods for gut health—from probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kefir to prebiotic-rich foods like garlic, onions, and apples—can improve digestion, enhance immune function, and reduce inflammation. By regularly including these foods in your meals, you can promote a thriving microbiome and support long-term digestive health.