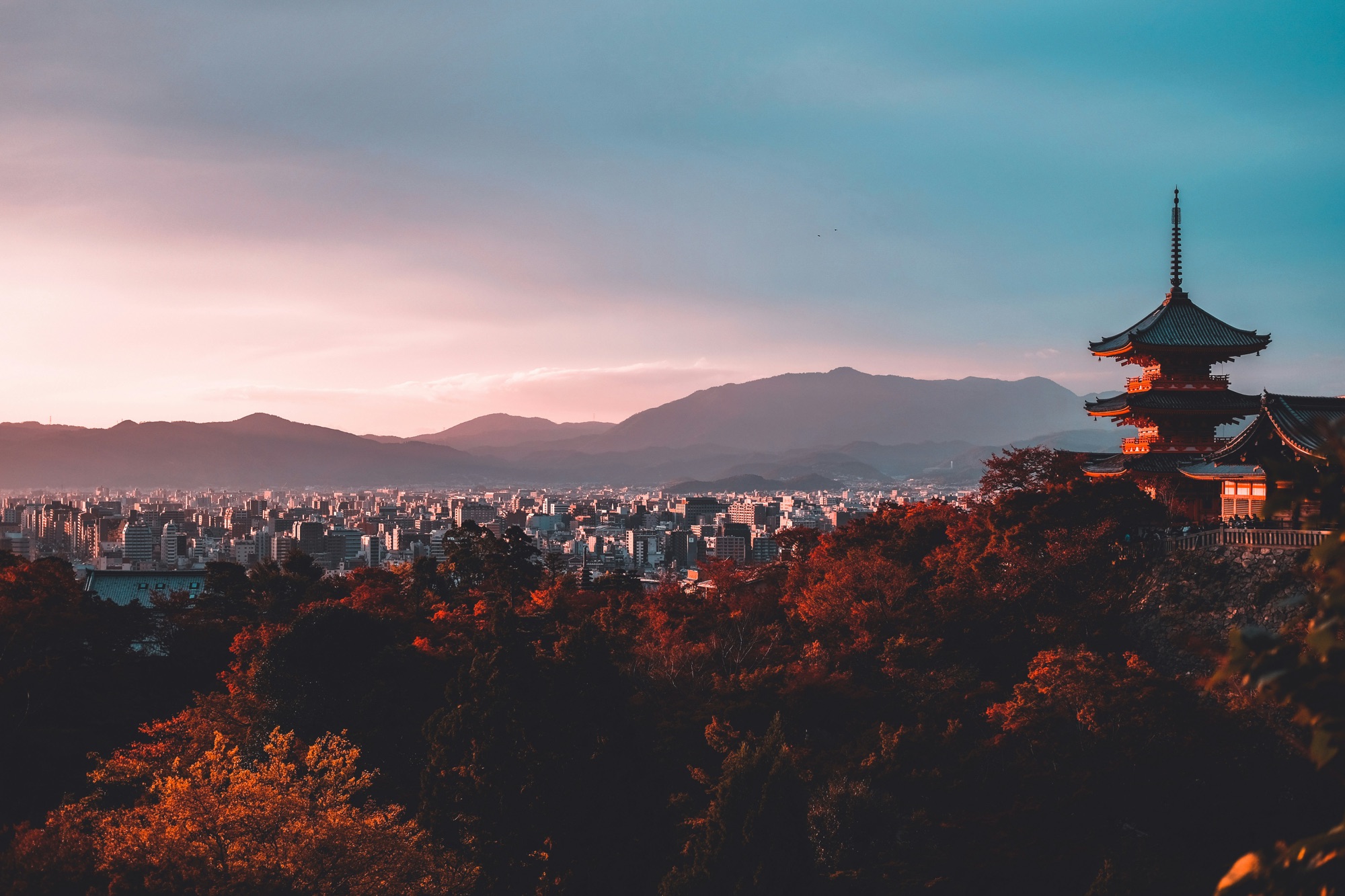
Japan is often referred to as the ‘Land of the Rising Sun,’ a title deeply rooted in the country’s cultural and historical significance. The name resonates with notions of hope, renewal, and the ever-present cycle of life, giving Japan a unique identity that captivates both its inhabitants and admirers worldwide.
Historical Origins
Geographic Position and Symbolism
The name ‘Land of the Rising Sun’ originates from Japan’s geographic location to the east of the Asian mainland. As Japan lies to the east of many other countries, it is often the first place to see the sunrise, symbolizing a new day and fresh beginnings. This geographical positioning has imbued the country with a sense of uniqueness and a metaphorical association with the dawn of a new era, both literally and metaphorically.
In ancient times, China’s imperial court referred to Japan as “Wa” or “Nihon,” which translates to “origin of the sun.” This reference highlights Japan’s position relative to China as the land where the sun rises. The significance of this eastward position continues to resonate through the ages, shaping Japan’s national narrative and identity.
The Influence of Geography on Culture
Japan’s geographical location has not only influenced its name but also its cultural development. The country’s island nature fostered a unique blend of isolation and openness, allowing for the development of distinctive cultural practices while also absorbing influences from neighboring countries. This blend is evident in Japan’s ability to innovate while respecting tradition, a characteristic that can be seen as an extension of its symbolic association with the sunrise.
Historical Texts and References
The concept of Japan as a land associated with the rising sun is not just a modern interpretation but is deeply embedded in historical texts. The Kojiki and Nihon Shoki, ancient chronicles of Japan, frequently mention the sun and its symbolism. These texts, dating back to the 8th century, are among the oldest historical records and provide insights into how integral the sun’s imagery was even in early Japanese culture.
Early Records and Mythology
The sun goddess Amaterasu is a central figure in Japanese mythology and is considered the ancestor of the imperial family. Her story is depicted in these ancient texts, where she emerges from a cave, bringing light to the world and signifying the birth of the Japanese nation. This mythological narrative reinforces the deep cultural ties between the sun and Japan’s identity, suggesting a divine origin for its people and their rulers.
Cultural Symbolism
Sun in Japanese Art and Literature
In Japanese culture, the image of the rising sun holds profound symbolic meaning. It is associated with vitality, renewal, and vigor, reflecting the country’s resilient spirit and unwavering determination. The rising sun also represents the idea of starting afresh each day, embracing new opportunities and challenges with optimism and strength.
This cultural significance is often reflected in various traditional arts:
- Noh Theater: In Noh performances, the sun may symbolize the triumph of light over darkness, a common theme that resonates with audiences.
- Tea Ceremonies: The rising sun is often seen as a metaphor for enlightenment and mindfulness, central themes in the ritual of tea.
- Haiku Poetry: The brevity and depth of haikus frequently capture the transient beauty of a sunrise, symbolizing fleeting moments of perfection.
Influence on Visual Arts
Japanese visual arts often incorporate the rising sun motif, not just as a direct representation but also as an underlying theme. Woodblock prints from the Edo period, for instance, frequently depicted dawn scenes, emphasizing the interplay of light and shadow. These prints were not only artistic expressions but also conveyed philosophical ideas about time, change, and the natural world.
Modern Cultural Interpretations
In contemporary Japan, the symbolism of the rising sun continues to influence various facets of life. From corporate logos that incorporate sun motifs to public holidays like New Year’s Day, which celebrate new beginnings, the rising sun remains a potent symbol. For instance, the Japanese flag, with its red circle on a white background, is known as the “Nisshoki” or “Hinomaru,” translating to “circle of the sun,” further emphasizing this cultural emblem.
Everyday Life and Traditions
In daily life, the rising sun’s symbolism is apparent in Japan’s cultural practices. The concept of “Asa-gohan,” or breakfast, is highly valued and symbolizes the start of a productive day, much like the dawn of a new day. Traditional breakfast dishes, such as miso soup and rice, are seen as providing the energy and balance needed to embrace the day ahead.
Imperial Connection
The Chrysanthemum Throne
Moreover, the rising sun emblem has been historically linked to Japan’s imperial family, further solidifying its association with the nation’s identity and heritage. The imperial family, known as the Chrysanthemum Throne, has used the rising sun motif as a symbol of their divine lineage and leadership throughout the centuries.
The connection between the imperial family and the rising sun symbolizes not only a political authority but also a spiritual connection to the celestial realm. This long-standing association has contributed to the enduring reverence and respect that the Japanese people hold for their imperial heritage and the symbols that represent it.
Symbolism in Ceremonies
Imperial ceremonies, such as the enthronement of a new emperor, often incorporate the rising sun motif. The sun’s imagery is used to convey messages of hope, renewal, and continuity, reflecting the emperor’s role as a stabilizing force in Japanese society. These ceremonies are steeped in tradition, with rituals that have been passed down through generations, further highlighting the symbolic importance of the sun in Japan’s national identity.
Historical Context and Modern Implications
The Meiji Restoration in the late 19th century was a pivotal moment when the rising sun symbol became more prominent in the national consciousness. During this period of rapid modernization and westernization, the emblem was used to signify Japan’s emergence as a new world power. Today, the Emperor’s role as a symbolic figurehead is intertwined with this imagery, representing continuity and tradition amidst change.
The Rising Sun in National Identity
The rising sun has played a crucial role in shaping Japan’s national identity, especially during times of transformation. In the Meiji era, the symbol was used to rally the nation around the idea of progress and modernization, serving as a beacon of hope and unity. This legacy continues to influence Japan’s self-image, as the country balances its rich heritage with the demands of a globalized world.
Economic and Technological Implications
Innovation as a New Dawn
Japan’s identity as the Land of the Rising Sun also ties into its reputation for innovation and technological prowess. The country’s commitment to pioneering new technologies can be seen as a metaphorical ‘rising sun’ in the global economic landscape. Companies like Sony, Toyota, and Nintendo have become synonymous with cutting-edge advancements, reflecting Japan’s role as a leader in bringing forth new ideas and products.
The Role of the Sun in Technological Development
The rising sun’s symbolism extends to Japan’s approach to technology and innovation. The concept of “Kaizen,” or continuous improvement, is deeply ingrained in Japanese business practices, mirroring the daily renewal associated with the sunrise. This mindset has driven Japan’s success in various industries, from electronics to automotive manufacturing, positioning the country as a global leader in innovation.
Sustainability and Future Prospects
Japan’s focus on sustainable development and renewable energy can also be viewed through the lens of its rising sun symbolism. The nation has made significant strides in solar energy, harnessing the literal power of the sun to fuel its future. Initiatives like the Solar Ark and ambitious projects for solar farms in space highlight Japan’s dedication to aligning its cultural heritage with modern environmental goals.
Solar Energy as a Symbol of Renewal
Japan’s commitment to solar energy is not just a practical choice but also a symbolic one. By embracing solar power, the country aligns itself with the idea of renewal and sustainability, drawing parallels with the rising sun’s promise of a new day. This approach reflects Japan’s ability to adapt and innovate while remaining true to its cultural roots.
Practical Tips for Visitors
Experiencing the Rising Sun in Japan
For those visiting Japan, witnessing the sunrise can be a deeply moving experience that connects travelers to the country’s spiritual and cultural roots. Here are a few tips to make the most of this experience:
- Climb Mount Fuji: Catching the sunrise from Japan’s highest peak is a quintessential experience. It’s best to start the ascent in the evening to reach the summit at dawn.
- Visit the East Coast Beaches: Places like Chiba and Ibaraki offer stunning views of the sunrise over the Pacific Ocean, perfect for early risers.
- Explore the Temples of Kyoto: Many temples open early, providing a serene setting to watch the sunrise amidst traditional architecture.
Immersive Sunrise Experiences
- Stay at a Ryokan: Traditional Japanese inns, or ryokans, often provide guests with a chance to enjoy the sunrise in a tranquil setting, complete with hot springs and beautiful gardens.
- Engage in Morning Meditation: Participating in a meditation session at a Zen temple during sunrise can offer a profound sense of peace and connection to the cultural significance of the rising sun.
Cultural Etiquette
When engaging with Japanese culture, especially in the context of its symbolism, it’s important to show respect and understanding. Simple gestures like bowing, removing shoes when entering homes or certain establishments, and using appropriate honorifics can go a long way in showing appreciation for Japan’s rich traditions.
Respecting Cultural Symbols
Visitors should also be mindful of the cultural significance of symbols like the rising sun. Participating in local customs, such as attending a sunrise festival or learning about the history behind the rising sun flag, can deepen one’s understanding and appreciation of Japan’s cultural heritage.
Common Misunderstandings
Avoiding Stereotypes
While the rising sun is a powerful symbol, it’s crucial to approach this imagery with sensitivity. The rising sun flag, for instance, has historical associations that may be viewed differently in various contexts, especially in countries affected by Japan’s actions during World War II. Understanding this duality is essential for appreciating the nuanced nature of cultural symbols.
Navigating Historical Context
To fully appreciate the symbolism of the rising sun, it’s important to acknowledge its complex history. Engaging with this symbol requires an awareness of its different interpretations and the ability to navigate its historical context with empathy and understanding.
Embracing Complexity
Japan’s identity as the Land of the Rising Sun is multifaceted, and while it is a source of national pride, it’s also intertwined with complex historical narratives. Engaging with these stories requires an open mind and a willingness to explore beyond surface-level interpretations.
Understanding the Layers of Meaning
The rising sun symbol is layered with meanings that extend beyond its immediate visual representation. By exploring its historical roots, cultural significance, and modern interpretations, one can gain a deeper appreciation for how this symbol continues to shape Japan’s national identity and influence its place in the world.
The moniker ‘Land of the Rising Sun’ encapsulates Japan’s geographical location, cultural symbols, and historical significance, embodying the essence of the country’s rich heritage and enduring spirit. It serves as a poignant reminder of Japan’s resilience, creativity, and deep-rooted traditions that continue to shape its identity and inspire people around the world. Through understanding this powerful symbol, we can gain greater insight into the Japanese way of life and the profound beauty that comes with the dawn of each new day.