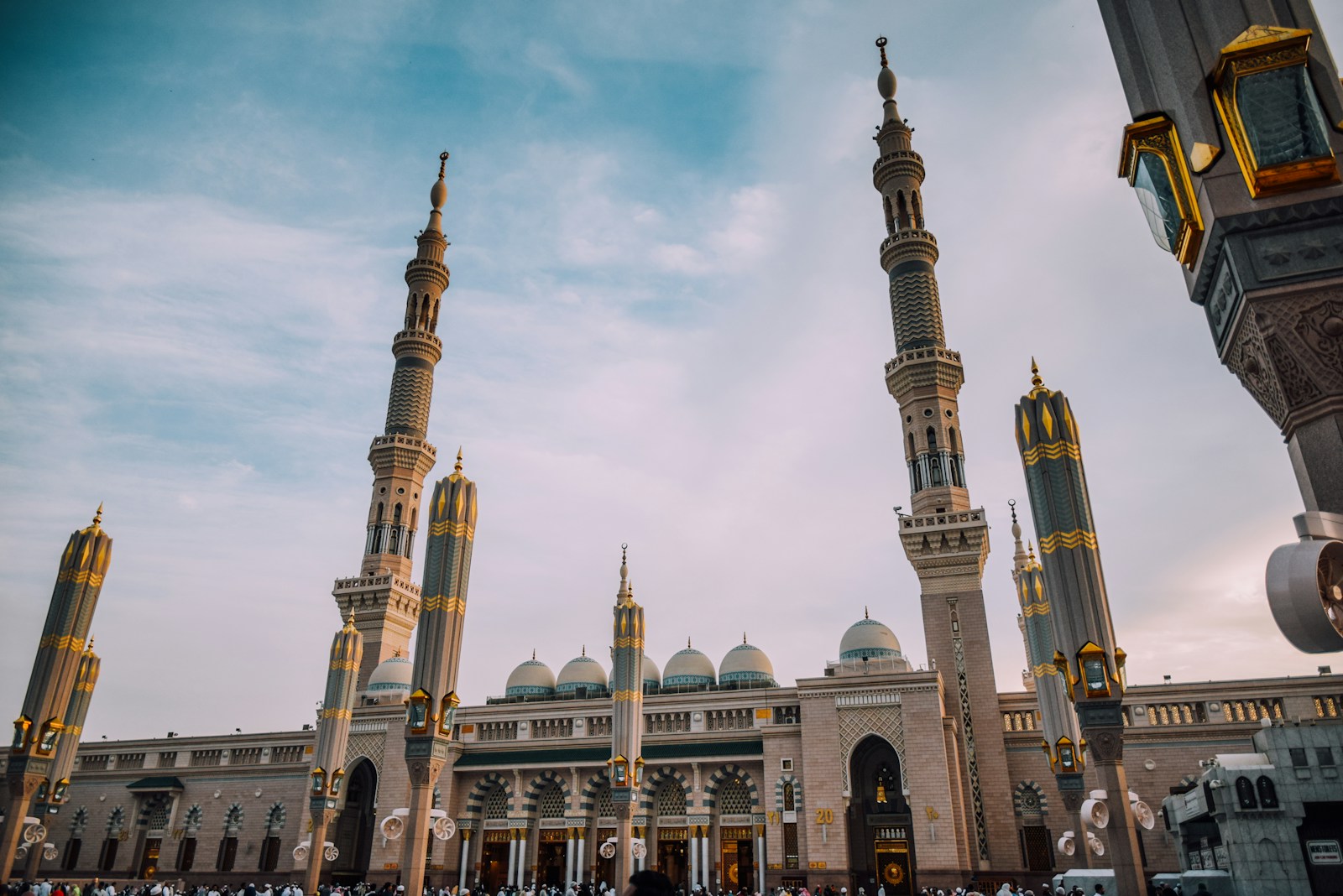
Saudi Arabia, the largest country in the Middle East, has long been a dominant player in regional and global politics due to its immense oil wealth, religious significance, and strategic position. As the birthplace of Islam and home to its two holiest cities, Mecca and Medina, Saudi Arabia wields considerable influence in the Muslim world. Its vast reserves of oil and natural gas have given it substantial economic clout, while its military modernization and regional alliances position it as a key security player in the Middle East.
In this article, we’ll examine Saudi Arabia’s economic, cultural, and military power, exploring how this resource-rich nation has built its influence and what challenges it faces in maintaining its position in an increasingly complex global landscape.
Economic Power: Oil Wealth and Vision 2030’s Diversification Efforts
Saudi Arabia’s economy has traditionally been built around its vast oil reserves, which have provided the kingdom with unparalleled wealth and influence in global markets. However, with fluctuating oil prices and growing global interest in renewable energy, Saudi Arabia is seeking to diversify its economy through ambitious reforms aimed at reducing its dependency on oil.
1. Oil as the Backbone of Saudi Arabia’s Economy
Saudi Arabia holds the world’s second-largest proven oil reserves, and its vast energy resources have made it the leading member of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). The country produces roughly 10 million barrels of oil per day, making it one of the largest oil exporters in the world. Oil accounts for around 70% of government revenues and a significant portion of its GDP.
Saudi Arabia’s state-owned oil company, Saudi Aramco, is the most valuable company in the world and plays a critical role in the kingdom’s economy. Aramco’s 2019 initial public offering (IPO) on the Tadawul stock exchange in Riyadh raised billions of dollars, reflecting the company’s importance not only to Saudi Arabia but to global energy markets.
Despite its reliance on oil, Saudi Arabia faces challenges related to the volatility of global oil prices, which have been affected by geopolitical tensions, shifting demand patterns, and the rise of renewable energy. As a result, the kingdom’s leaders have recognized the need to diversify its economy and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels.
2. Vision 2030: A Blueprint for Economic Diversification
In 2016, Saudi Arabia launched Vision 2030, an ambitious reform plan aimed at transforming its economy by reducing its reliance on oil and developing other sectors such as tourism, entertainment, technology, and renewable energy. The plan, spearheaded by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, seeks to create a more sustainable and diversified economy while promoting private sector growth and attracting foreign investment.
Key elements of Vision 2030 include:
- Neom, a futuristic mega-city project that aims to become a global hub for innovation, technology, and sustainable living.
- Tourism initiatives, such as opening Saudi Arabia to international tourists and developing its Red Sea coastline into a major tourism destination.
- Promoting domestic industries such as mining, manufacturing, and defense to reduce reliance on imports.
- Expanding the role of women in the workforce and implementing social reforms aimed at increasing workforce participation.
While progress has been made, challenges remain in fully implementing Vision 2030. The kingdom’s economic reforms have been met with resistance from conservative factions, and global economic conditions, such as the COVID-19 pandemic and fluctuations in oil prices, have slowed the pace of change. However, Vision 2030 represents a clear shift in Saudi Arabia’s long-term economic strategy.
3. Foreign Investment and Economic Partnerships
Saudi Arabia’s efforts to diversify its economy have been accompanied by a push to attract foreign investment and build international partnerships. The kingdom has sought to deepen ties with countries such as China, Japan, and the United States, particularly in sectors like energy, defense, and infrastructure development.
Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund (PIF), the country’s sovereign wealth fund, is a key vehicle for promoting economic diversification. The PIF has made significant investments in global companies and projects, including Uber, Lucid Motors, and SoftBank’s Vision Fund. By leveraging its oil wealth, Saudi Arabia aims to build a portfolio of international investments that can support its transition to a post-oil economy.
4. Challenges to Economic Diversification
Despite its ambitious plans, Saudi Arabia faces several challenges in reducing its reliance on oil. The global shift toward renewable energy and efforts to combat climate change could reduce demand for oil in the coming decades, potentially impacting the kingdom’s primary source of revenue. Additionally, while the government has implemented reforms aimed at promoting private sector growth, the economy remains heavily dependent on the public sector.
Moreover, unemployment remains a significant issue, particularly among young Saudis, and the government must address the growing demands for jobs and social services from its youthful population. Finally, Saudi Arabia’s dependence on foreign labor, particularly in the construction and service sectors, poses challenges to developing a more self-sufficient economy.
Cultural Power: The Custodian of Islam’s Holiest Sites and the Global Influence of Saudi Arabia’s Soft Power
Saudi Arabia’s cultural power is deeply rooted in its status as the birthplace of Islam and its role as the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques in Mecca and Medina. This religious significance gives Saudi Arabia considerable influence over the global Muslim community. However, the kingdom is also working to expand its cultural influence beyond religion, particularly through efforts to promote entertainment, tourism, and modern cultural initiatives.
1. Islamic Leadership and Religious Influence
Saudi Arabia’s role as the custodian of Mecca and Medina, the two holiest cities in Islam, gives it unparalleled religious influence in the Muslim world. Every year, millions of Muslims from around the world travel to Saudi Arabia for the Hajj pilgrimage, which is one of the five pillars of Islam. The kingdom’s management of the Hajj and its control over Islamic sites elevate its status among Muslim-majority countries and reinforce its soft power.
Saudi Arabia also plays a key role in promoting Wahhabism, a conservative interpretation of Sunni Islam, through its global network of mosques, schools, and Islamic institutions. While this has bolstered Saudi influence in many parts of the Muslim world, it has also drawn criticism for fostering religious extremism in some cases.
2. Cultural Diplomacy and Saudi Arabia’s Global Image
In recent years, Saudi Arabia has sought to reform its image on the global stage, moving away from its strict conservative identity toward a more modern and globally engaged society. Part of this effort includes a cultural transformation driven by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman. These changes include the loosening of social restrictions, such as allowing women to drive, opening cinemas, and promoting entertainment events like music concerts and sporting events.
The kingdom has also invested in sports diplomacy, hosting international events like the Formula E races, WWE wrestling events, and boxing matches. In 2020, Saudi Arabia made headlines when it successfully bid to host the Dakar Rally, further raising its profile in the global sports arena.
These efforts are part of a broader campaign to boost tourism and soft power, with Saudi Arabia seeking to become a cultural and tourism destination in the Middle East. By promoting modern cultural initiatives and engaging in cultural diplomacy, Saudi Arabia aims to reshape its image and appeal to a global audience.
3. Entertainment and the Opening of Society
As part of Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia has made significant strides in opening up its entertainment sector. The creation of the General Entertainment Authority (GEA) in 2016 marked a shift in the kingdom’s approach to culture and entertainment, with the government investing heavily in the development of new entertainment infrastructure, such as theme parks, concert venues, and theaters.
The lifting of the 35-year ban on cinemas in 2018 was a symbolic moment in Saudi Arabia’s cultural transformation, as it opened the door to a new era of cultural expression and entertainment within the kingdom. Major film festivals, including the Red Sea International Film Festival, have since been launched, drawing international attention to Saudi Arabia’s emerging cultural scene.
These changes have been met with mixed reactions domestically, as conservative factions within the country remain resistant to the rapid pace of reform. Nevertheless, the kingdom’s efforts to promote entertainment and cultural openness represent a significant departure from its historically conservative social structure.
4. Challenges to Cultural Power
While Saudi Arabia’s cultural reforms have generated excitement, they have also faced significant challenges. The country’s human rights record, particularly regarding freedom of expression, women’s rights, and the treatment of political dissidents, has drawn international criticism. The 2018 murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi at the Saudi consulate in Istanbul damaged the kingdom’s reputation and raised concerns about its commitment to reform.
Moreover, the rapid pace of social change has created tension within Saudi society, where conservative elements resist the reforms being implemented by the government. The balancing act between modernization and maintaining traditional values will continue to be a challenge for Saudi Arabia as it seeks to navigate its cultural evolution.
Military Power: A Key Regional Player with Ambitions to Modernize
Saudi Arabia’s military power is a critical component of its influence in the Middle East. The kingdom has invested heavily in modernizing its armed forces, making it one of the largest military spenders in the world.
While Saudi Arabia lacks the military capabilities of global superpowers, its defense spending and strategic alliances, particularly with the United States, give it significant regional clout.
1. Saudi Arabia’s Military Spending and Modernization
Saudi Arabia is consistently one of the world’s top military spenders, with defense expenditures exceeding $67 billion annually. This spending has allowed the kingdom to acquire advanced military technology, including fighter jets, missiles, tanks, and naval vessels. Much of Saudi Arabia’s military hardware is purchased from Western countries, particularly the United States, the United Kingdom, and France.
Saudi Arabia’s military modernization efforts are part of its strategy to become more self-reliant in defense. Under Vision 2030, the kingdom has set a goal to localize 50% of its military spending by developing a domestic defense industry. The creation of the Saudi Arabian Military Industries (SAMI) is part of this effort, with the company working on developing domestic production of military equipment and technology.
2. The Saudi-Led Coalition in Yemen
Saudi Arabia has been involved in the conflict in Yemen since 2015, leading a coalition of Arab states in support of the Yemeni government against Houthi rebels, who are backed by Iran. The war in Yemen has been a critical test of Saudi Arabia’s military capabilities, but it has also drawn international criticism for the humanitarian crisis it has created. The conflict has resulted in tens of thousands of civilian casualties and widespread destruction, leading to calls for a ceasefire and a negotiated settlement.
The war in Yemen is part of Saudi Arabia’s broader effort to counter Iran’s regional influence, which Riyadh views as a major threat to its security. The conflict has demonstrated Saudi Arabia’s willingness to project military power beyond its borders, but it has also revealed the limitations of its military capabilities, particularly in conducting sustained operations.
3. Strategic Alliances and U.S. Military Support
Saudi Arabia’s military strength is closely tied to its strategic alliance with the United States. The U.S. provides Saudi Arabia with advanced military equipment, training, and intelligence support, particularly in the context of countering Iranian influence in the region. The U.S.-Saudi military relationship has been a cornerstone of the kingdom’s defense strategy since the 1940s.
In addition to its relationship with the U.S., Saudi Arabia has forged alliances with other Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states, including the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain, as part of its efforts to maintain regional security. These alliances are aimed at countering threats from Iran and extremist groups like ISIS.
4. Challenges to Military Power
Despite its significant military spending, Saudi Arabia faces several challenges in translating its military investments into effective power projection. The conflict in Yemen has exposed weaknesses in Saudi Arabia’s ability to conduct asymmetric warfare and achieve decisive victories in complex conflicts. Additionally, the kingdom’s reliance on foreign military suppliers raises concerns about its long-term military self-sufficiency.
Furthermore, Saudi Arabia’s regional rivalry with Iran continues to pose significant security challenges, as the two countries vie for influence across the Middle East. Saudi Arabia’s participation in proxy conflicts, such as those in Syria, Lebanon, and Iraq, further complicates its security landscape and underscores the difficulties of maintaining stability in a volatile region.
Conclusion: Saudi Arabia’s Power in a Shifting Global Landscape
Saudi Arabia’s power is built on a combination of vast oil wealth, religious significance, and military spending, positioning it as a key player in the Middle East and beyond. Economically, Saudi Arabia’s dominance in global energy markets gives it significant leverage, while its efforts to diversify through Vision 2030 demonstrate a recognition of the need to prepare for a post-oil future. Culturally, the kingdom wields considerable influence as the custodian of Islam’s holiest sites, while its efforts to modernize and open its society have attracted international attention.
Militarily, Saudi Arabia’s significant defense spending and strategic alliances make it a formidable force in the region, though challenges remain in translating this investment into long-term military efficacy. The kingdom’s rivalry with Iran, its involvement in regional conflicts, and its reliance on foreign military support are ongoing issues that will shape its military and geopolitical strategy in the years to come.
As Saudi Arabia continues to navigate the complexities of its economic transformation and regional security challenges, its ability to balance modernization with traditional values, economic diversification with global market dynamics, and military strength with diplomatic alliances will determine its place in the future global order.