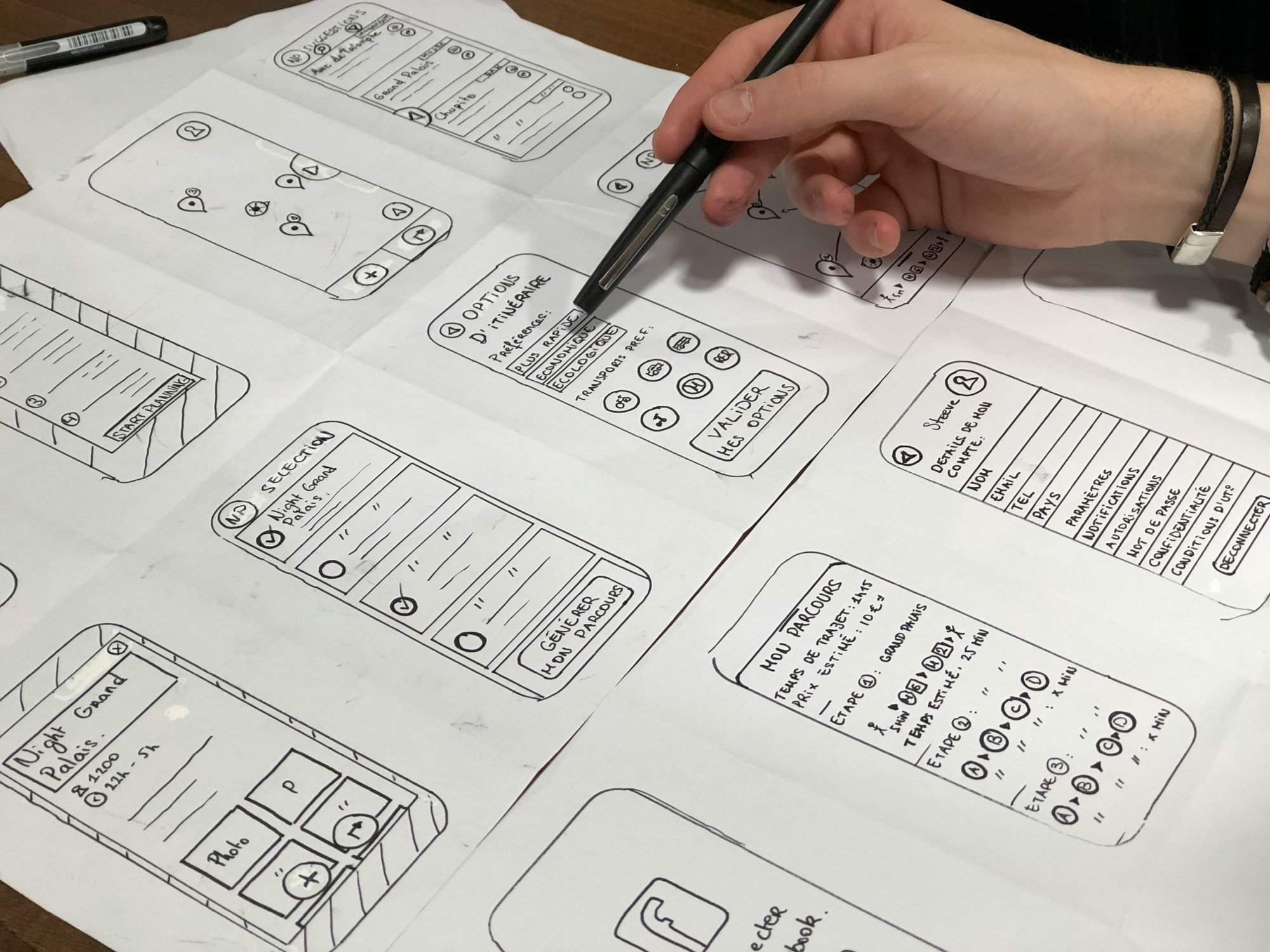
Navigating the world of digital product design can feel a bit like trying to differentiate between identical twins at a family reunion. They look similar, share a lot of the same DNA, and yet, they each have unique traits and roles. In the digital design ecosystem, we’re talking about UX designers, UI designers, and web designers. While all three aim to create engaging and user-friendly digital experiences, the paths they take to get there are distinct. Let’s dive deeper into these roles, explore their specific responsibilities, and help you figure out which one you might need for your next project.
UX Designer: Crafting Seamless Journeys
The Core Focus of UX Design
Imagine walking into a new store. The layout, the ease with which you find what you’re looking for, and the overall feeling you get from the space—this is the domain of the UX designer. They’re like the architects of digital experiences, focusing on how users interact with a product and ensuring that every step of the journey is as intuitive and enjoyable as possible.
Responsibilities of a UX Designer
- User Research: This is where it all begins. UX designers dive deep into understanding their audience through interviews, surveys, and usability testing. For example, if designing an app for seniors, they might conduct face-to-face interviews to gauge ease of use and accessibility needs.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Think of wireframes as the blueprint of your digital product. They sketch out the skeletal framework, while prototypes bring these blueprints to life for testing. Tools like Figma or Sketch are common allies in this phase.
- Information Architecture: UX designers organize content and functionalities to enhance usability. This might involve creating user flows or sitemaps to ensure that users can navigate the product effortlessly.
- User Testing & Feedback: Testing isn’t a one-off task. UX designers continuously test and refine products, employing methods like A/B testing to tweak and perfect the user experience.
- Collaboration with Developers and UI Designers: A UX designer doesn’t work in isolation. They’re in constant conversation with UI designers and developers to ensure the product’s functionality aligns with its visual design.
- Accessibility Considerations: They ensure that products are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This might mean incorporating screen reader capabilities or ensuring color contrast ratios are compliant with accessibility standards.
Key Skills Required
- Mastery in user research methodologies
- Expertise in wireframing and prototyping
- Strong analytical thinking and problem-solving skills
- Understanding of behavioral psychology and cognitive science
- Usability testing and A/B testing expertise
Real World Example
Consider a project for a travel booking app. A UX designer might start by conducting surveys to understand user frustrations with existing platforms—perhaps users find it hard to compare flight prices. Armed with this insight, the designer creates wireframes that prioritize clear, side-by-side price comparisons. User testing might reveal that users struggle with the checkout process, prompting further refinements to make the payment steps more intuitive.
UI Designer: The Art of Visual Delight
The Core Focus of UI Design
If UX designers are the architects, UI designers are the interior decorators. They transform the framework into an engaging, cohesive design that aligns with the brand’s identity. Their work ensures that every interface is not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing.
Responsibilities of a UI Designer
- Visual Design: Creating interfaces that are not just beautiful but also intuitive. This involves selecting color schemes, fonts, and design elements that enhance the user’s experience.
- Typography and Color Theory: UI designers choose fonts and colors that reflect the brand and promote readability. For instance, a financial app might use calm blues and greens to convey trust and security.
- Interactive Design: Buttons, icons, and animations fall under this umbrella. The goal is to create a seamless interactive experience that feels natural to the user.
- Consistency in Design Systems: Ensuring that design elements are uniform across all pages and screens. This might include creating a style guide for future updates.
- Brand Identity Integration: UI designers ensure that the design reflects the company’s brand and tone, maintaining consistency across all digital platforms.
- Design for Different Devices: Optimizing designs for various screen sizes is crucial, as users might switch between their phone, tablet, and desktop.
Key Skills Required
- Proficiency in visual design principles
- Advanced skills in design tools like Adobe XD, Figma, and Sketch
- Basic understanding of front-end development
- Keen attention to detail and creativity
- Knowledge of animation and motion design
Practical Tips
- Stay Updated with Trends: The design world is ever-evolving. UI designers should keep an eye on emerging trends to ensure their designs feel fresh and modern.
- Use Design Systems: Employing a design system can speed up the design process and ensure consistency. Tools like Material Design offer ready-to-use components that can be customized to fit the brand.
- Prototype Interactions: Before finalizing, prototype interactive elements like hover states or transitions to see how they feel in action. This can prevent costly redesigns later.
Web Designer: The Digital Craftsman
The Core Focus of Web Design
Web designers wear many hats. They straddle the line between design and development, ensuring that a website is not only visually appealing but also functional and responsive. Unlike UX and UI designers, who might focus on apps or software, web designers specifically bring websites to life.
Responsibilities of a Web Designer
- Website Layout and Aesthetics: Crafting interfaces that are engaging and easy to navigate. This involves both visual design and the technical know-how to implement it.
- Responsive Design: Making sure websites work seamlessly across devices. This might include using flexible grid layouts or media queries in CSS.
- HTML/CSS Implementation: Web designers often write or modify front-end code to bring designs to fruition. Knowledge of JavaScript can also be beneficial.
- SEO Considerations: Optimizing a site for search engines is crucial. This might involve structuring content with SEO in mind or ensuring fast load times.
- Collaboration with Developers and Content Creators: Working closely with other stakeholders to ensure the website meets both aesthetic and functional requirements.
- Website Speed Optimization: Fast load times are critical for user satisfaction and SEO. Techniques like image compression or lazy loading can help.
Key Skills Required
- Proficiency in graphic design and visual storytelling
- Front-end coding skills (HTML, CSS, JavaScript)
- Knowledge of web accessibility standards
- Familiarity with CMS platforms like WordPress or Webflow
- Understanding of SEO best practices
Real World Example
Imagine a project for a local bakery launching its first website. A web designer would begin by discussing the bakery’s brand and goals. They might design a homepage with high-quality images of the baked goods, ensuring that the layout is mobile-friendly. After building the site using a CMS like WordPress, they’d optimize images and use plugins to improve site speed, all while ensuring that the site ranks well on search engines.
UX Designer vs. UI Designer vs. Web Designer: A Closer Look
Role Intersections and Collaborations
While UX, UI, and web designers have distinct roles, their work often overlaps, requiring seamless collaboration. For example:
- Product Launch: In a new product launch, UX designers might start with user research and wireframes, which are then handed off to UI designers to craft the visual identity. Web designers might step in later to ensure the product’s website aligns with the design and user experience goals.
- Design Systems: UX and UI designers might collaborate on creating a design system that ensures consistency across digital products. Web designers can then use these systems to maintain brand consistency on websites.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Project
Identifying the right professional for your project depends on your specific needs:
- Improving User Experience: If your focus is on enhancing how users interact with your product, a UX designer is your go-to.
- Enhancing Visual Appeal: To boost the aesthetic appeal and ensure interface consistency, engage a UI designer.
- Building a Website: For designing and developing a functional, responsive website, you need a web designer.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Overlapping Roles Without Clear Boundaries: It’s crucial to define each designer’s role clearly to prevent confusion and ensure efficient teamwork.
- Neglecting User Feedback: Failing to incorporate user feedback can lead to designs that don’t meet user needs. Continuous testing and iteration are key.
- Ignoring Mobile Users: In a mobile-first world, ensuring your designs are responsive and mobile-friendly is non-negotiable.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re a business looking to hire or an aspiring designer seeking your niche, understanding the distinct roles of UX, UI, and web designers is crucial. Each brings unique skills to the table, and their combined efforts result in digital products that are not only beautiful but also effective and user-friendly. By recognizing these differences and fostering collaboration, you can create digital experiences that truly resonate with users.